Documentation
Introduction
DNSSEC/TLSA Validator allows you to check the existence and validity of DNSSEC-signed DNS records. If a valid DNSSEC chain related to the requested domain has been found the plug-in will also check for the existence and validity of TLSA records. TLSA records store hashes of the remote server TLS/SSL certificates. The authenticity of a TLS/SSL certificate for a given domain name is verified by the DANE protocol (RFC 6698). DNSSEC and TLSA validation results are presented using various icons. Additional explanatory texts are displayed in the page’s address bar (MF and GC) or in a separate toolbar (IE). Clicking on a given icon symbol reveals more detailed information about the state of security. The screen-shots are available here.
DNSSEC states
The colour of the key icon signals whether the domain name is secured by DNSSEC. List of available key colours and description of corresponding states are as follows:

For an existing domain name this means that this domain name is not secured by DNSSEC. It is not possible to verify the validity of obtained DNS data and you are not secured against domain name spoofing. For a non-existent domain name it means that the parent domain is not secured by DNSSEC. Thus, it was not possible to verify the non-existence of such domain name.

For an existing domain name this means that this domain name is correctly secured by DNSSEC. Information about the IP address of related to this domain name was validated using DNSSEC. You are protected against domain name spoofing because this domain name is secured by DNSSEC. For a non-existent domain name it means that the parent domain is secured by DNSSEC. Thus, it was possible to successfully verify the non-existence of this domain name.

For an existing domain name this means that this domain name is secured by DNSSEC but an invalid domain name signature has been detected. For a non-existent domain name it means that the parent domain is secured by DNSSEC but the received non-existence response does not contain a valid signature. In both cases this may signalise a domain name spoofing attempt.

For an existing domain name this means that this domain name is secured by DNSSEC. But, the IP address which the browser is using differs from the address obtained by the DNSSEC add-on. This may have a legitimate reason but can also point at a DNS spoofing attempt. IP addresses differences can be caused by a proxy (cache) server that your browser uses for obtaining the desired page.

The DNSSEC validation for this domain was not performed because you have enabled the domain-name filter and the domain name or its parent domain was found in the list of excluded domains. This state is shown as well when DNSSEC validation is fully disabled.

Initialization of DNSSEC Validator or non-active browser window or tab.

An error occurred while getting the DNSSEC status of this domain name. This may be caused by the loss of connection to the DNS server or the user-chosen validating resolver IP address is not an address of a validating resolver. This state also occur if an unexpected error during the validation process is detected. It may also occur during web browsing if the DNS server or the resolver, which is currently being used, does not support DNSSEC. Typically this issue can occur when using a wireless connection and the user moves between several WIFI connections without restarting the browser. In such situation, you should change the validator settings. Set a custom resolver which supports DNSSEC data forwarding (e.g., 8.8.8.8), or you can also use the 'Without resolver' choice.

The domain name DNSSEC status resolution is pending.
DANE/TLSA states
For DANE/TLSA validation, the possible padlock icon colours and corresponding states are as follows:

For an existing domain name this means that no HTTPS secured connection to the remote server was established. Therefore, you can not perform TLSA record validation. The authenticity of TLS/SSL remote server certificate for the domain name could not be verified by DANE protocol because the connection to the remote server is not realized via HTTPS protocol.

For an existing domain name this means that TLSA record for this domain name is not secured by DNSSEC. Therefore, it is not possible to verify the validity of remote server certificate by DANE protocol.

For an existing domain name this means that the remote server certificate for this domain name could not be verified by DANE protocol because there is no TLSA record for this domain name.

For an existing domain name this means that the authenticity of remote server TLS/SSL certificate for this domain name was verified by DANE protocol. The certificate corresponds to TLSA record which is secured by DNSSEC technology.

For an existing domain name this means that the DANE protocol verification of remote server's certificate for this domain name failed. The certificate does not correspond to the TLSA record which is secured by DNSSEC technology. This can be caused by trying to connect to an untrusted remote server or an invalid server certificate.

The TLSA validation for this domain was not performed because you have enabled the domain filter and this domain name or its parent domain was found in the list of excluded domains. This state is shown as well when TLSA validation is fully disabled.

Initialization of TLSA Validator or non-active browser window or tab.

An error occurred while getting the DANE/TLSA status of this domain name. This may be caused by the loss of connection to the DNS server or the user-chosen validating resolver IP address is not an address of a validating resolver. This state also occur if an unexpected error during the validation process is detected. It may also occur during web browsing if the DNS server or the resolver, which is currently being used, does not support DNSSEC. Typically this issue can occur when using a wireless connection and the user moves between several WIFI connections without restarting the browser. In such situation, you should change the validator settings. Set a custom resolver which supports DNSSEC data forwarding (e.g., 8.8.8.8), or you can also use the 'Without resolver' choice.

The DANE/TLSA status resolution is pending.
Validator settings
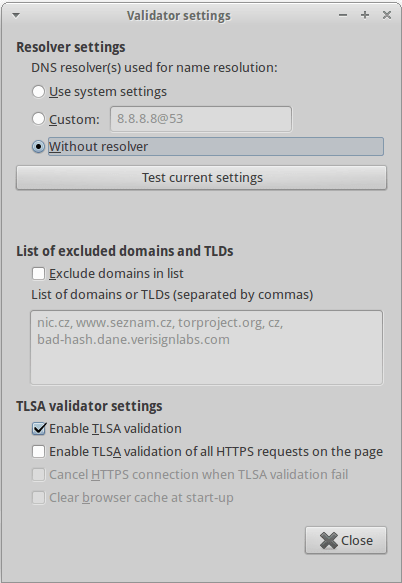
In the settings you can set the DNS resolver used for obtaining DNSSEC/TLSA data. Also, you are allowed to set a list of excluded top-level domain (TLD) or domain mames which will not be validated by DNSSEC/TLSA plug-in. Note that by default the choice 'without resolver' is used. This value will provide correct behaviour of the validation process on most internet connections. For faster validation, you can use the default system resolver. If the system resolver is not able to handle DNSSEC data you will need to set a custom resolver or select the choice 'without resolver'.
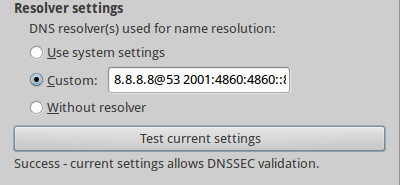
You can specify a space-separated list of resolver IP addresses (with port numbers) (e.g.: 8.8.8.8 8.8.4.4@53 2001:4860:4860::8844). These resolvers will be used for DNSSEC/TLSA data forwarding if selected. You may test whether your current setting supports DNSSEC by pressing the test button.
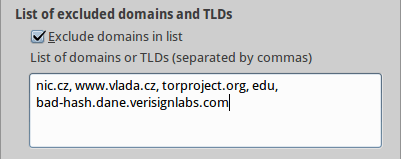
You may also use a domain-name filter. If the check-box of excluded domains is enabled, the TLDs (e.g.: cz, org, com) or domain names (www.nic.cz, example.com, bad-hash.dane.verisignlabs.com, etc.) specified in the text area will not be validated using DNSSEC. Specified domain names must be separated by commas and spaces (i.e.: example.com, nic.cz, org, eu). Please note that domains which are sub-domains of the listed domains won't also be validated. ('fedoraproject.org' won't be vaidated if 'org' is in the list.)

You can disable or enable the validation of TLSA records. If TLSA validation is enabled validation process will be provided only for domain the name which is shown in the address bar. Using this setting the TLSA causes the page to be loaded more quickly.
With the second check box you can select whether the TLSA validator will be check all HTTP requests. This will slightly decrease the loading speed because every HTTPS established connection will be checked by TLSA validator. In this mode, you may choose whether to block the HTTPS connection when TLSA validation fails (using the third check box). In such case, a pop-up dialog will be generated.
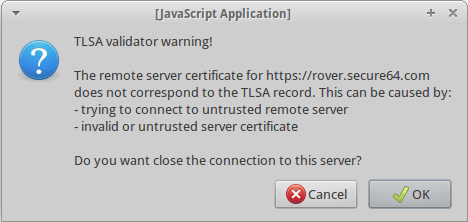
The connection to the remote server can be cancelled by clicking the OK button. You may choose to ignore this message by clicking the Cancel button. Once the content of the page is loaded the warning dialog will not be shown again until the browser cache is erased or the browser is restarted.
Troubleshooting & Debug
If you encounter any troubles while using the DNSSEC/TLSA validator turn the debugging messages on to see what's happening.
Mozilla Firefox
The browser's about:config menu contains items named extensions.dnssec.dnssecdebug and extensions.dnssec.danedebug. Find these items using the search field and switch them to "true" by double-clicking them. Then start Firefox from a terminal or cmd.exe (in case of Windows).
firefox -no-remote -console -P
All DNS queries and responses from and to DNSSEC/TLSA Validator will be dumped to the terminal along with other debugging messages.
Google Chrome
Start Chrome browser from terminal and via Settings->Extensions find the DNSSEC and TLSA Validator extensions. Then click on '_generated_background_page.html' link and choose the Console.
google-chrome
All DNS queries and responses of the DNSSEC and TLSA Validator cores will be printed out to the terminal along with other debugging messages. Debug messages generated by javascript code will be printed into javascript Console.
Internet Explorer
In order to debug the plug-in you must use MS Visual Studio (support for ALTRACE).
